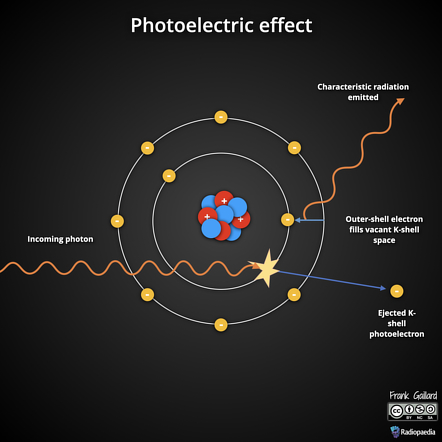
The photoelectric effect is the phenomenon in which electrons are emitted from a material—usually a metal—when it is exposed to light of sufficiently high frequency. This effect shows that light can behave as particles (called photons), each carrying a specific amount of energy. If a photon has enough energy, it can knock an electron out of the material. The photoelectric effect provided key evidence for quantum theory and helped establish the idea that light has both wave-like and particle-like properties.
- Teacher: Jean Damascene NDIKURYAYO

